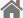Sliding bearings, bearings that work under sliding friction. It is characterized by stable, reliable and noise-free operation. In
the following operating conditions: 1 Load weight 2 Accuracy Extra 3
High speed rpm 4 Extra large or small 5 Special structure (required
bearing part) Plain bearings have advantages over rolling bearings. Therefore,
sliding bearings are often used in steam turbines, centrifugal
compressors, internal combustion engines, and large motors. In addition, low-speed and impacted machines (such as cement mixers, crushers, etc.) are also commonly used as plain bearings.
Sliding bearing structure
►Integral Radial Slide Bearing
Features: simple structure, low cost.
The gap between the journal and the bearing bore after wear cannot be
adjusted; it can only be installed and disassembled in the axial
direction
Applications: In machines with low speed, light load or intermittent operation.
► Split bearing
Features: easy to install the bearing, the gap can be adjusted, but the structure is complex.
Note: The angle between the vertical line and the radial force of part
of the surface shall not be greater than 35°. Otherwise, the 45°
inclined part is used.
► Thrust sliding bearing
Thrust sliding bearings consist of a bearing seat and a thrust journal. Commonly used journal structure:
Hollow type: The pressure distribution on the journal contact surface
is even and the lubrication condition is better than the solid type.
Single ring type: The annular end surface of the journal is used as
the thrust surface, which is simple in structure, easy to lubricate, can
withstand dual-core, and widely used in low-speed and low-load
applications.
Multi-ring type: The bearing capacity is large and it can withstand two-way axial load. However, the load distribution among the rings is not uniform.
Bearing structure
Bearings
should have a certain strength and rigidity, to be fixed and reliable,
good lubrication, heat dissipation, easy loading and unloading and
adjustment. The
bearing shell is fixed on the bearing seat. The surface of the bearing
shell is often cast with a layer of anti-friction material to become the
bearing lining. The thickness is from a few millimeters to six
millimeters. In order to make the bearing lining secure, grooves can be made in the bearing bush.
►Forms and construction of bearings
Integral type: sleeve
Partial type:
1 thick-walled bearing: wall thickness/diameter>0.05
2 thin wall bearings: wall thickness / outside diameter
► Bearing positioning
The relative displacement of the bearing shell and the bearing housing is not allowed.
The fixed method can be used:
a. Both ends are flanged.
b. Set screws or pins.
c. Partially punch out the locating lip.
► Fitting of bearing shell and bearing seat
In order to improve the rigidity of the bearing shell, heat
dissipation and concentricity with the bearing seat hole, a tight
interference fit is generally used.
► oil trench and oil tank
In
order to introduce the lubricant into the entire friction surface, an
oil groove or oil groove is required on the bush or journal. The length of the axial oil groove should be slightly shorter than the
width of the bearing bush! The liquid lubricates the bearing and the
oil groove does not open in the pressure zone, otherwise the continuity
and load bearing capacity of the oil film are damaged.
Bearing and bearing lining material
Bushes and bearing lining materials are collectively referred to as bearing materials.
► Requirements for bearing materials
Good abrasion resistance, abrasion resistance and bite resistance
Good friction compliance, embeddedness and wearability
Adequate strength and corrosion resistance
Good thermal conductivity, processability, economy, etc.
There
are few materials that can satisfy the above requirements at the same
time. In engineering, casting or pressing methods are used to combine
two different metals together to complement each other in performance. The commonly used bushings and bearing lining materials are the following:
1) Bearing alloy (known as babbitt or white alloy)
a. Tin-bearing bearing alloy
b. Copper-tin alloy
2) Bronze
3) Special performance bearing materials
a、Oil bearing
b, cast iron
c, rubber bearing
d, plastic bearings
Commonly used bearing pads and bearing lining materials performance table
Lubricant selection
The
purpose of bearing lubrication is to reduce frictional power
consumption, reduce wear, and also play a role in cooling shock
absorption and rust prevention. Whether the bearing can work normally has a lot to do with whether the lubricant is used correctly or not.
Lubricants are divided into:
Liquid Lubricant - Lubricating Oil
Semi-solid lubricant - grease
Solid lubricant
CATEGORIES
Latest news
- Ferrofluid Vacuum Feedthrough Seals us
- Which one is wear-resistant, steel sle
- Bimetal Flange Bush Bearing
- Selection standard for dimension refer
- Red color ptfe bushing
- Pipe-Mounted Ball Transfer
Contact us
- ADD: No.503,Hunan International Commerce Center, Jintai Square,Changsha 410001,Hunan.
- TEL: +86 731 84770165
- FAX: +86 731 84770163
- E-mail: sales1@slide-bearing.com